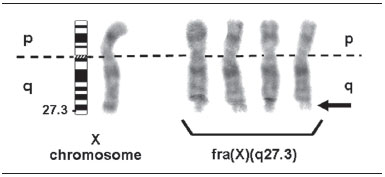
The tip of the iceberg: what is hidden under the fragile X
Maria de Lourdes ChauffailleJ. Bras. Patol. Med. Lab. 2017;53(2):80DOI: 10.5935/1676-2444.20170015 English PDF Full text
The tip of the iceberg: what is hidden under the fragile X Read More »