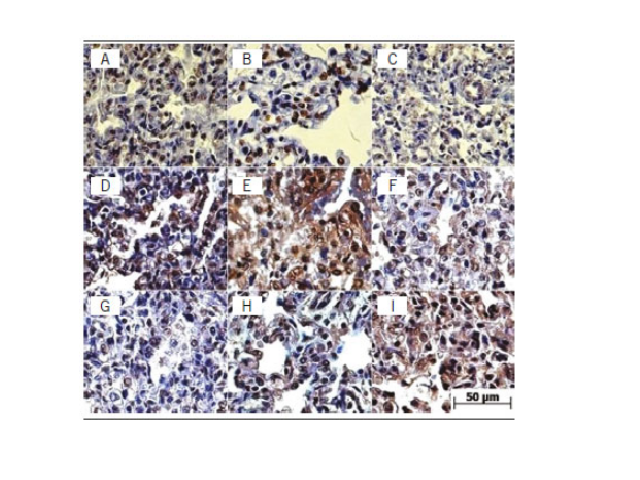
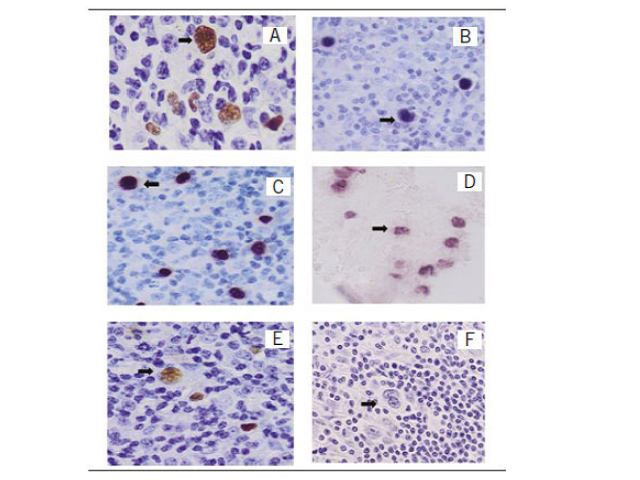
Diet and cancer
Adagmar AndrioloJ. Bras. Patol. Med. Lab. 2016;52(6):366DOI: 10.5935/1676-2444.20160059 Cancer is a complex group of diseases with numerous possible causes. These include genetic factors, eating habits, lifestyle, viral infections, exposure to different types of potentially mutagenic agents and radiation, among others. Although it represents an important group, cancers arising from inherited gene mutations correspond to a […]