Implementation of criteria for automatic release of clinical chemistry test results in a laboratory at an academic public hospital
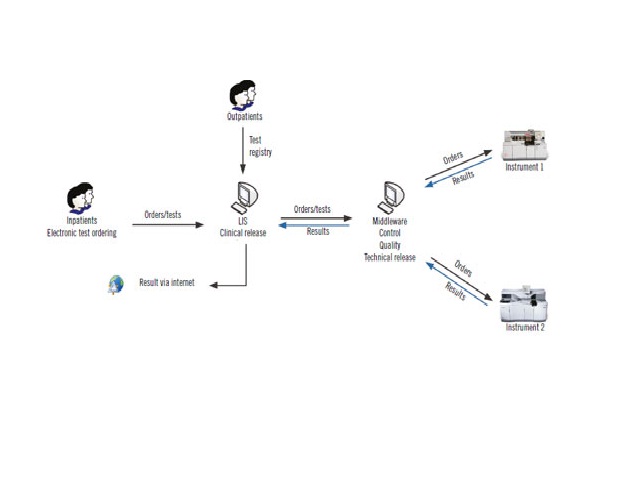
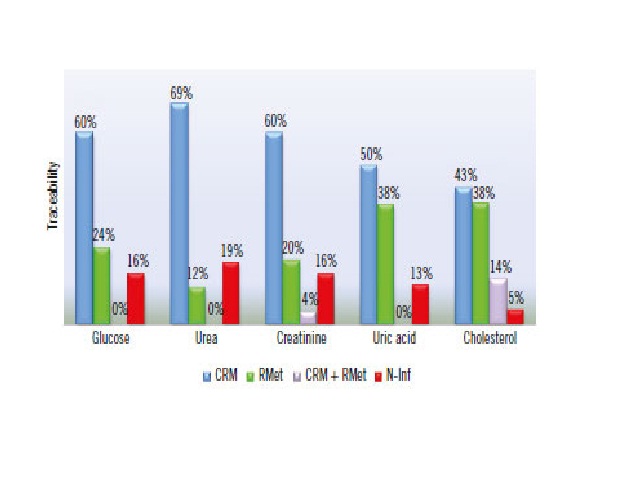
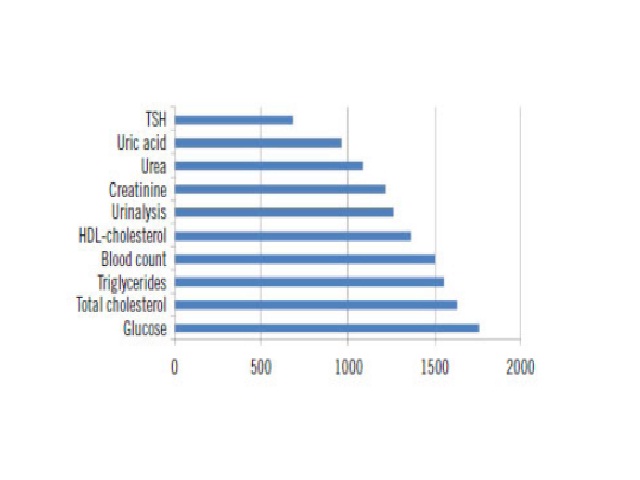
Myriam S. Feitosa; Daniel Henrique Bücker; Silvana Maria E. Santos; Leonardo S. VasconcellosJ. Bras. Patol. Med. Lab. 2016;52(3):149-156DOI: 10.5935/1676-2444.20160026 ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION: Autoverification is the release of laboratory test results from clinical instruments to hospital interface, or to patients’ records, with no human intervention. Verification rules are inserted in the middleware and/or in the laboratory information system […]