Use of ischemia modified albumin for the diagnosis of myocardial infarction
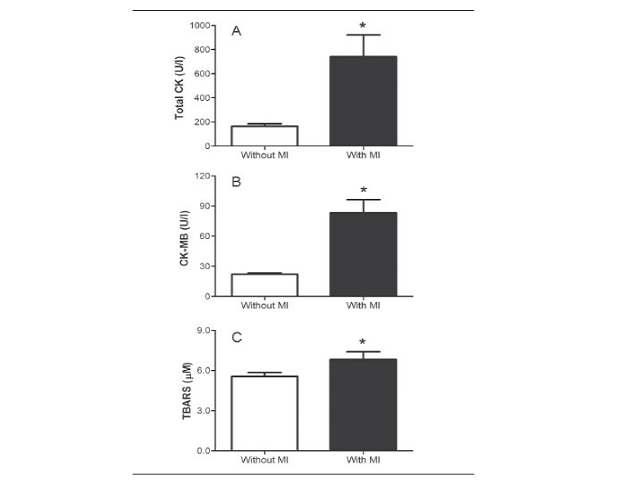
Nariélle F. Bonorino; Adroaldo Lunardelli; Jarbas R. OliveiraJ. Bras. Patol. Med. Lab. 2015;51(6):383-388DOI: 10.5935/1676-2444.20150060 ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION: Literature reports addressing ischemia modified albumin (IMA) as a good marker for the early diagnosis of myocardial ischemia through albumin cobalt binding (ACB) test, that is before myocardial infarction (MI) occurs.OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the IMA plasmatic levels in infarcted patients, in […]
Use of ischemia modified albumin for the diagnosis of myocardial infarction Read More »