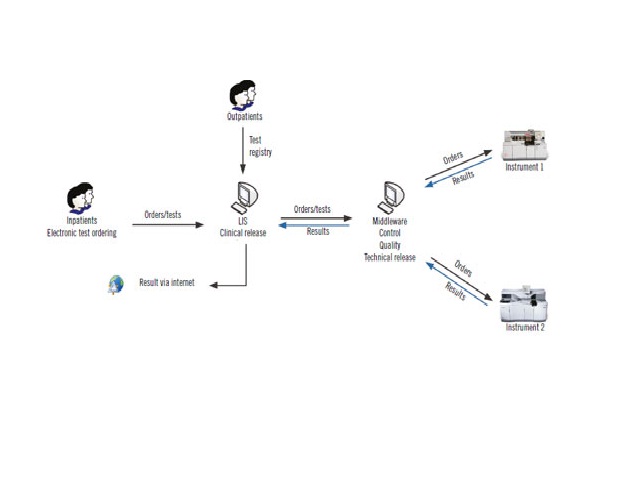
Implementation of criteria for automatic release of clinical chemistry test results in a laboratory at an academic public hospital
Implantação de critérios de liberação automática de resultados de bioquímica em um laboratório de hospital público universitário Myriam S. Feitosa1; Daniel Henrique Bücker1; Silvana Maria E. Santos2; Leonardo S. Vasconcellos2 1. Hospital das Clínicas da Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais (HC/UFMG), Minas Gerais, Brazil2. Falcudade de Medicina da UFMG, Minas Gerais, Brazil DOI: 10.5935/1676-2444.20160026 Corresponding […]